ui5-typescript-walkthrough
Step 20: Data Types
The list of invoices is already looking nice, but what is an invoice without a price assigned? Typically prices are stored in a technical format and with a ‘.’ delimiter in the data model. For example, our invoice for pineapples has the calculated price 87.2 without a currency. We are going to use the OpenUI5 data types to format the price properly, with a locale-dependent decimal separator and two digits after the separator.
Preview
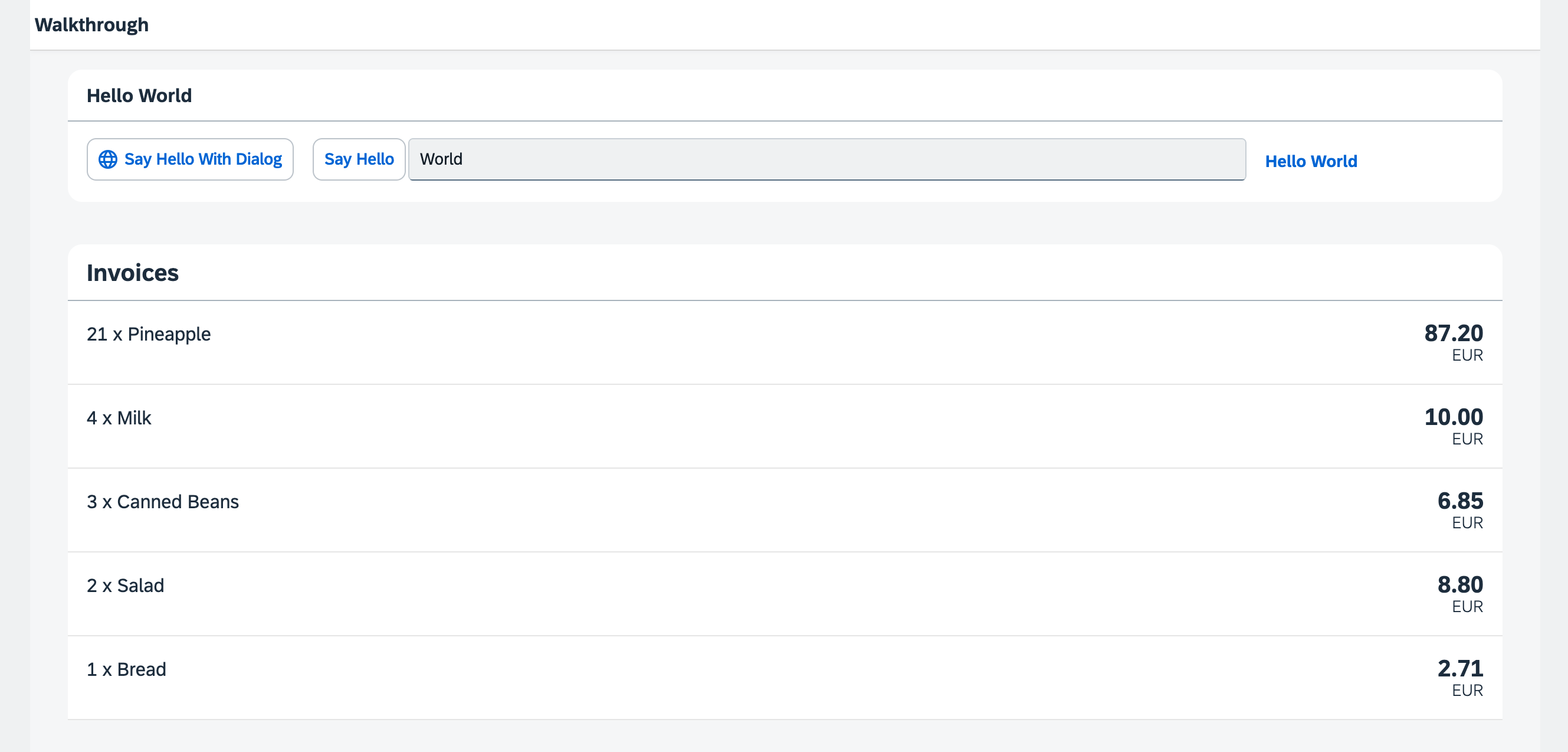
The list of invoices with prices and number units
You can access the live preview by clicking on this link: 🔗 Live Preview of Step 20. ***
Coding
webapp/controller/InvoiceList.controller.?s (New)
We want to display in our list view the price in Euro. Since currency information isn’t available in our backend data model, we’ll handle the currency formatting within the application.
We’ll create a controller for the InvoiceList view and use a JSON model (sap/ui/model/json/JSONModel) to store the currency code. This model will contain a single property, currency: "EUR", which will be used for formatting the prices in the view.
import Controller from "sap/ui/core/mvc/Controller";
import JSONModel from "sap/ui/model/json/JSONModel";
/**
* @namespace ui5.walkthrough.controller
*/
export default class App extends Controller {
onInit(): void {
const viewModel = new JSONModel({
currency: "EUR"
});
this.getView()?.setModel(viewModel, "view");
}
};
sap.ui.define(["sap/ui/core/mvc/Controller", "sap/ui/model/json/JSONModel"], function (Controller, JSONModel) {
"use strict";
const App = Controller.extend("ui5.walkthrough.controller.App", {
onInit() {
const viewModel = new JSONModel({
currency: "EUR"
});
this.getView()?.setModel(viewModel, "view");
}
});
;
return App;
});
webapp/view/InvoiceList.view.xml
We add the invoice list controller to the view to get access to the view model we defined in the controller.
We add a price and the currency to our invoices list in the view by adding the number attribute to the ObjectListItem control. To apply the currency data type, we use the require attribute with the namespace URI sap.ui.core, for which the prefix core is already defined in our XML view. This allows us to write the attribute as core:require. We then add the currency data type module to the list of required modules and assign it the alias Currency, making it available for use within the view. Then we set the type attribute of the binding syntax to the alias Currency. The Currency type will handle the formatting of the price for us, based on the currency code. In our case, the price is displayed with 2 decimals.
Additionally, we set the formatting option showMeasure to false. This hides the currency code in the property number. Instead we pass the currency on to the ObjectListItem control as a separate property numberUnit.
<mvc:View
controllerName="ui5.walkthrough.controller.InvoiceList"
xmlns="sap.m"
xmlns:core="sap.ui.core"
xmlns:mvc="sap.ui.core.mvc">
<List
headerText="{i18n>invoiceListTitle}"
class="sapUiResponsiveMargin"
width="auto"
items="{invoice>/Invoices}" >
<items>
<ObjectListItem
core:require="{
Currency: 'sap/ui/model/type/Currency'
}"
title="{invoice>Quantity} x {invoice>ProductName}"
number="{
parts: [
'invoice>ExtendedPrice',
'view>/currency'
],
type: 'Currency',
formatOptions: {
showMeasure: false
}
}"
numberUnit="{view>/currency}"/>
</items>
</List>
</mvc:View>
As you can see above, the example uses a special binding syntax for the number property of the ObjectListItem. This binding syntax uses Composite Binding, which allows you to bind multiple properties from different models to a single control property. The properties bound from different models are called parts. In the example above, the control property is number and the bound properties (parts) are retrieved from two different models: invoice>ExtendedPrice and view>/currency.
Convention
- Use data types instead of custom formatters whenever possible.
Next: Step 21: Expression Binding
Previous: Step 19: Aggregation Binding
Related Information
Composite Binding
Formatting, Parsing, and Validating Data
Require Modules in XML View and Fragment
API Reference: sap.ui.base.ManagedObject
API Reference: sap.ui.base.ManagedObject.PropertyBindingInfo
API Reference: sap.ui.model.type